The Sydney’s Salty Communities program, through funding from the Australian Government, has allowed SCCG and partners to support on-ground projects at local and sub-regional scales to address pressures from pollution, weeds, feral animals, degradation, neglect, inundation and erosion. Coastal land managers have used strategic assessment and conservation management activities to physically assess, restore, enhance and maintain biodiversity values and functions in these critical areas. The Salty program has issued 17 grants worth a little over $1.25 million for projects valued at over $2.75 million. Additionally, research projects have been funded to identify gaps in regional coastal biodiversity management knowledge and practice, and into climate change readiness.
Quick Navigation
Fact sheets & tools
Fact sheets
Sydney’s Salty Communities has distilled key information (gathered for, or deriving from, aspects of the program) into a series of fact sheets.









Tools






Main Round Grants
There were eleven successful applicants for the Main Round of Grants. Their proposals aim to restore and enhance Sydney Metro’s Salty Community biodiversity in a wide variety of settings, using measures both innovative and well-tested. In total almost $950,000 was awarded on projects valued at just over $2 million. The successful projects are:
SSC_01 Urban aquatic corridors
City of Sydney Council
 The City of Sydney partnered with The University of Sydney’s Centre for Research on Ecological Impacts of Coastal Cities and the Royal Botanic Gardens & Domains Trust to create an aquatic corridor along the seawall foreshore of the City of Sydney local government area. This project delivered 60 seawall pots that were further developed from previous designs to accelerate the process of colonising these habitat structures. School visits introduced hundreds of school children to key concepts around marine habitat creation. A successful Ecological Engineering Forum showcased a variety of interventions from around the world to support inter-tidal biodiversity. This grant project has now been successfully completed and part of its legacy is the research coming from this trial.
The City of Sydney partnered with The University of Sydney’s Centre for Research on Ecological Impacts of Coastal Cities and the Royal Botanic Gardens & Domains Trust to create an aquatic corridor along the seawall foreshore of the City of Sydney local government area. This project delivered 60 seawall pots that were further developed from previous designs to accelerate the process of colonising these habitat structures. School visits introduced hundreds of school children to key concepts around marine habitat creation. A successful Ecological Engineering Forum showcased a variety of interventions from around the world to support inter-tidal biodiversity. This grant project has now been successfully completed and part of its legacy is the research coming from this trial.
SC_04 Gore Creek Reserve bush management
Lane Cove Council
 Bush regeneration contractors were engaged to remove weed species & encourage regeneration of native species in Gore Creek Reserve, focusing on endangered Littoral Rainforest and surrounds. Weed species to be controlled in the reserve included: ground asparagus, morning glory, madeira vine, Ehrharta, Trad, Privet & Ochna. Gore Creek Reserve Bushcare group and others have worked alongside the contractors with the aim of restoring bushland adjacent to their work sites. This project has been successfully completed and the legacy of the project will be maintained in the years to come through Lane Cove Council’s commitment of ongoing designated operational budget for the area, as well as the efforts of the local BushCare groups.
Bush regeneration contractors were engaged to remove weed species & encourage regeneration of native species in Gore Creek Reserve, focusing on endangered Littoral Rainforest and surrounds. Weed species to be controlled in the reserve included: ground asparagus, morning glory, madeira vine, Ehrharta, Trad, Privet & Ochna. Gore Creek Reserve Bushcare group and others have worked alongside the contractors with the aim of restoring bushland adjacent to their work sites. This project has been successfully completed and the legacy of the project will be maintained in the years to come through Lane Cove Council’s commitment of ongoing designated operational budget for the area, as well as the efforts of the local BushCare groups.
SSC_09 N. Palm Beach dune rehabilitation
Pittwater Council

 The North Palm Beach Dune Rehabilitation project rehabilitated 5.9ha (50% more than target) of highly degraded coastal dune within the North Palm Beach dune system. Managing weeds in the target site was important in tackling what was a reservoir of weeds threatening other rehabilitated and remnant vegetation. Over 5,000 native tubestock were planted. Completion of this project has reconnected a well-functioning native ecosystem and improved cological linkages between remnant native vegetation. This grant project has now been successfully completed and the legacy of the project will be maintained in the years to come through Northern Beaches Council’s commitment of ongoing designated operational budget for the area, as well as the efforts of local BushCare groups.
The North Palm Beach Dune Rehabilitation project rehabilitated 5.9ha (50% more than target) of highly degraded coastal dune within the North Palm Beach dune system. Managing weeds in the target site was important in tackling what was a reservoir of weeds threatening other rehabilitated and remnant vegetation. Over 5,000 native tubestock were planted. Completion of this project has reconnected a well-functioning native ecosystem and improved cological linkages between remnant native vegetation. This grant project has now been successfully completed and the legacy of the project will be maintained in the years to come through Northern Beaches Council’s commitment of ongoing designated operational budget for the area, as well as the efforts of local BushCare groups.
SSC_10 Bilgola Creek biodiversity
Pittwater Council
 The project addressed major weed infestations within the project area. Two EECs were targeted: Themeda Grasslands on Coastal Headlands and Littoral Rainforest & Coastal Vine Thickets. Revegetation at 3 sites controlled exotic grasses at South Bilgola Headland, providing littoral restoration of the Bilgola Creek and restoring Coastal Clay Heath within an area heavily invaded by bamboo. A community planting and information day was held along the Bicentennial Walkway track, which was also be upgraded to limit damage to the Themeda grassland. Over 2,250 native tubestock and 2kg of Themeda seed were planted. This grant project has now been successfully completed and the legacy of the project will be maintained in the years to come through Northern Beaches Council’s commitment of ongoing designated operational budget for the area, as well as the efforts of local BushCare groups.
The project addressed major weed infestations within the project area. Two EECs were targeted: Themeda Grasslands on Coastal Headlands and Littoral Rainforest & Coastal Vine Thickets. Revegetation at 3 sites controlled exotic grasses at South Bilgola Headland, providing littoral restoration of the Bilgola Creek and restoring Coastal Clay Heath within an area heavily invaded by bamboo. A community planting and information day was held along the Bicentennial Walkway track, which was also be upgraded to limit damage to the Themeda grassland. Over 2,250 native tubestock and 2kg of Themeda seed were planted. This grant project has now been successfully completed and the legacy of the project will be maintained in the years to come through Northern Beaches Council’s commitment of ongoing designated operational budget for the area, as well as the efforts of local BushCare groups.
SSC_11 Integrated fox control
Rockdale City Council

 This project has brought together 11 physically connected Councils (Bayside, Cumberland, City of Canada Bay, City of Canterbury Bankstown, Georges River, Inner West, Randwick, Strathfield, City of Sydney, Sutherland Shire & Waverley) and Royal Botanic Gardens Sydney (RBGS) to coordinate a regional approach to fox management through a Fox Control Working Committee. SSROC have taken over management of this Committee to continue its work. A web portal, foxscan.org.au has been set up to allow residents to report fox sightings across the region. During the project at least 150 foxes were removed from the region. RBGS has established a monitoring program for the committee, to answer core research questions about fox distribution, movements, predation, diet, behavioural elements. Community education and engagement and the trialing of fox control measures have been initiated in the project period.
This project has brought together 11 physically connected Councils (Bayside, Cumberland, City of Canada Bay, City of Canterbury Bankstown, Georges River, Inner West, Randwick, Strathfield, City of Sydney, Sutherland Shire & Waverley) and Royal Botanic Gardens Sydney (RBGS) to coordinate a regional approach to fox management through a Fox Control Working Committee. SSROC have taken over management of this Committee to continue its work. A web portal, foxscan.org.au has been set up to allow residents to report fox sightings across the region. During the project at least 150 foxes were removed from the region. RBGS has established a monitoring program for the committee, to answer core research questions about fox distribution, movements, predation, diet, behavioural elements. Community education and engagement and the trialing of fox control measures have been initiated in the project period.
SSC_17 Waverly coastal heath
Waverley Council
 The Waverley Council LGA has lost 99% of the remnant vegetation that was present before European Settlement. This project is part of a larger effort by Waverley Council to halt this loss and improve the condition of the remnant from the current 4% up to 40% by 2020. To implement Council’s newly adopted ‘Biodiversity Action Plan – Remnant Sites’. This project involved planting buffer and connectivity revegetation around our remnants. Over 42,000 native tubestock were planted. This will result in improved remnant condition, increased flora diversity
The Waverley Council LGA has lost 99% of the remnant vegetation that was present before European Settlement. This project is part of a larger effort by Waverley Council to halt this loss and improve the condition of the remnant from the current 4% up to 40% by 2020. To implement Council’s newly adopted ‘Biodiversity Action Plan – Remnant Sites’. This project involved planting buffer and connectivity revegetation around our remnants. Over 42,000 native tubestock were planted. This will result in improved remnant condition, increased flora diversity and a reduction in invasive weeds, particularly along the coastal cliff-top heath vegetation communities. In combination with revegetation plantings the outcome has been an increased in size and resilience of the remnant vegetation communities. This grant project has now been successfully completed and the legacy of the project will be maintained for at least the next five years through Waverley Council’s commitment of ongoing designated operational budget for the area, as well as through the efforts of local BushCare groups.
and a reduction in invasive weeds, particularly along the coastal cliff-top heath vegetation communities. In combination with revegetation plantings the outcome has been an increased in size and resilience of the remnant vegetation communities. This grant project has now been successfully completed and the legacy of the project will be maintained for at least the next five years through Waverley Council’s commitment of ongoing designated operational budget for the area, as well as through the efforts of local BushCare groups.
SSC_18 Willoughby salty ecosystems
Willoughby City Council
 The project has improved connectivity between three zones located along the Lane Cove R. starting from the Fullers Rd bridge next to the Lane Cove National Park moving south through O.H. Reid Reserve, the Chatswood Golf Course and Mowbray Park. Work primarily consisted of invasive weed removal to allow natural regeneration of indigenous species and this was supplemented with some plantings of indigenous plants to strengthen connection of work zones and other saltmarsh areas along the Lane Cove R. Willoughby City Council matched the contribution from Sydney’s Salty Communities grant to deliver this important project to rehabilitate this impacted ecosystem. 2,600 native tubestock were planted (800 more than target) and 8.9ha of weed treatment was undertaken. This grant project has now been successfully completed and the legacy of the project will be maintained in the future through Willoughby Council’s commitment of ongoing designated operational budget for the area, and the ongoing relationship they have developed with Chatswood Golf Club.
The project has improved connectivity between three zones located along the Lane Cove R. starting from the Fullers Rd bridge next to the Lane Cove National Park moving south through O.H. Reid Reserve, the Chatswood Golf Course and Mowbray Park. Work primarily consisted of invasive weed removal to allow natural regeneration of indigenous species and this was supplemented with some plantings of indigenous plants to strengthen connection of work zones and other saltmarsh areas along the Lane Cove R. Willoughby City Council matched the contribution from Sydney’s Salty Communities grant to deliver this important project to rehabilitate this impacted ecosystem. 2,600 native tubestock were planted (800 more than target) and 8.9ha of weed treatment was undertaken. This grant project has now been successfully completed and the legacy of the project will be maintained in the future through Willoughby Council’s commitment of ongoing designated operational budget for the area, and the ongoing relationship they have developed with Chatswood Golf Club.
SSC_20 Sydney’s living shorelines
OceanWatch

 Through this project, waste oyster shell collected from commercial farms were processed and arranged to protect eroding riverbanks and to stabilise riparian and coastal vegetation. For the purposes of the Salty Communities Program, erosion control and vegetation enhancement is the primary objective. The project was carried out on behalf of 4 councils – Willoughby, Lane Cove, Sutherland Shire and City of Ryde, and involves education, with community groups engaged in reef building activities. Macquarie University is currently undertaking research into the performance of different oyster reef structures, & will build these project sites into their research program. Preliminary testing of the structures has been undertaken at UNSW’s Water Research Laboratory at Manly Vale. This project is ongoing due to delays in obtaining the required permits to install the reefs. Pleasingly, more test sites are being pursued with the support of Greater Sydney Local Land Services.
Through this project, waste oyster shell collected from commercial farms were processed and arranged to protect eroding riverbanks and to stabilise riparian and coastal vegetation. For the purposes of the Salty Communities Program, erosion control and vegetation enhancement is the primary objective. The project was carried out on behalf of 4 councils – Willoughby, Lane Cove, Sutherland Shire and City of Ryde, and involves education, with community groups engaged in reef building activities. Macquarie University is currently undertaking research into the performance of different oyster reef structures, & will build these project sites into their research program. Preliminary testing of the structures has been undertaken at UNSW’s Water Research Laboratory at Manly Vale. This project is ongoing due to delays in obtaining the required permits to install the reefs. Pleasingly, more test sites are being pursued with the support of Greater Sydney Local Land Services.
SSC_21 Mosman foreshore biodiversity
Mosman Council
This project involved undertaking bushland regeneration and natural area restoration works around the foreshore of Quakers Hat Park and Harnett Park including rope access work. This work will act to protect, enhance and connect corridors along the foreshores and protect against a heat island affect under climatic changes. Residents were involved in a pilot Native Havens Program, where council supports residents to create native gardens that support wildlife through offering advice, native indigenous tubestock, and ongoing support in habitat protection. More than 4,600 native tubestock were planted (54% more than target). A baseline survey of intertidal flora and fauna was also undertaken. This grant project has now been successfully completed and the legacy of the project will be maintained through Mosman Council’s commitment of ongoing designated operational budget for the area, as well as through the efforts of the local Native Havens group they are developing with residents.
SSC_22 Woronora River resilience
Sutherland Shire Council

 Located in the Woronora River valley area (Woronora to Heathcote), the project has reduced the impacts of aggressive weed species, Weeds of National Significance & Key Threatening Processes on threatened flora and fauna species & three Endangered Ecological Communities of Coastal Saltmarsh, Swamp Oak Flood Plain Forest & Swamp Sclerophyll Forest on Coastal Floodplains. The activities have enhanced the 9 sites’ native biodiversity, increase public empowerment/knowledge and ensure past inappropriate urban development is ameliorated to ensure the ecosystem health of one of Sydney’s most unique Riverine systems. The project significantly exceeded its targets: pest management was undertaken in over 200ha of bushland (44% above target); weed treatment was implemented in 85ha (21% above target), and; over 2,100 native tubestock were planted (114% above target). This grant project has now been successfully completed and the legacy of the project will be maintained for at least the next ten years through Sutherland Shire Council’s commitment of ongoing designated operational budget for the area, as well as its long-term Woronora River Management Plan.
Located in the Woronora River valley area (Woronora to Heathcote), the project has reduced the impacts of aggressive weed species, Weeds of National Significance & Key Threatening Processes on threatened flora and fauna species & three Endangered Ecological Communities of Coastal Saltmarsh, Swamp Oak Flood Plain Forest & Swamp Sclerophyll Forest on Coastal Floodplains. The activities have enhanced the 9 sites’ native biodiversity, increase public empowerment/knowledge and ensure past inappropriate urban development is ameliorated to ensure the ecosystem health of one of Sydney’s most unique Riverine systems. The project significantly exceeded its targets: pest management was undertaken in over 200ha of bushland (44% above target); weed treatment was implemented in 85ha (21% above target), and; over 2,100 native tubestock were planted (114% above target). This grant project has now been successfully completed and the legacy of the project will be maintained for at least the next ten years through Sutherland Shire Council’s commitment of ongoing designated operational budget for the area, as well as its long-term Woronora River Management Plan.
SSC_23 Balls Head Reserve Canopy Recovery
North Sydney Council
 The remnant canopy of Balls Head has been affected by termites which appears to be having a serious ring-barking effect on many of these trees. To avoid generational loss of canopy this project involved research to compare treatment of arboreal termites (Nasutitermes walkeri) with appropriate control sites to compare tree responses and determine cause and effect for poor tree health. There has been a formalised monitoring regime, implemented by the School of Science at ACU, to record and assess short and long-term responses in tree health that alleviating termite damage will achieve. Bush regeneration work has been undertaken to remediate damage. Particularly pleasing in this project is that, by developing best practice methods with a consulting arborist, the project was able to be delivered with only a third the grant amount, while also extending the area treated to Berry Island (an increase in area of over 30%). The arborist’s report is available for download (PDF, 1.3MB).
The remnant canopy of Balls Head has been affected by termites which appears to be having a serious ring-barking effect on many of these trees. To avoid generational loss of canopy this project involved research to compare treatment of arboreal termites (Nasutitermes walkeri) with appropriate control sites to compare tree responses and determine cause and effect for poor tree health. There has been a formalised monitoring regime, implemented by the School of Science at ACU, to record and assess short and long-term responses in tree health that alleviating termite damage will achieve. Bush regeneration work has been undertaken to remediate damage. Particularly pleasing in this project is that, by developing best practice methods with a consulting arborist, the project was able to be delivered with only a third the grant amount, while also extending the area treated to Berry Island (an increase in area of over 30%). The arborist’s report is available for download (PDF, 1.3MB).
While it will take some years to know the full impact of the intervention on the health of the canopy at these two sites, the legacy of the project will be maintained through Council’s commitment of ongoing designated operational budget for the area, and through the ongoing collaborative work between NSC and the School of Science at ACU.
Supplementary Round Grants
The Supplementary Round of Grants was targeted to better focus the program on collaboration and climate change adaptation. Six grants with a total value of just over $303,000 were awarded, for projects to the value of almost $737,000.
SSC_24 Dee Why Lagoon
biodiversityWarringah Council
 This project supported an ongoing whole-of-lagoon approach, by focussing on the southern area of the refuge through restoring saltmarsh, creating habitat linkages and controlling vertebrate pest animals. This project has • Reduced the spread of high priority weeds; • Promoted a backyard habitat and garden escapes program; • Promoted the DY Fauna Fair as a celebration of the Wildlife Refuge for lagoon users; • Established a native seed bank using provenance from Dee Why Lagoon and neighbouring lagoon systems; • Produced a condition map of the bushland and saltmarsh, including mapping tree hollows. This project complements the ‘Dee Why Lagoon Wildlife Refuge Habitat Restoration Project’, a three year program funded through Environmental Trust.
This project supported an ongoing whole-of-lagoon approach, by focussing on the southern area of the refuge through restoring saltmarsh, creating habitat linkages and controlling vertebrate pest animals. This project has • Reduced the spread of high priority weeds; • Promoted a backyard habitat and garden escapes program; • Promoted the DY Fauna Fair as a celebration of the Wildlife Refuge for lagoon users; • Established a native seed bank using provenance from Dee Why Lagoon and neighbouring lagoon systems; • Produced a condition map of the bushland and saltmarsh, including mapping tree hollows. This project complements the ‘Dee Why Lagoon Wildlife Refuge Habitat Restoration Project’, a three year program funded through Environmental Trust.
SSC_25 Warriewood Wetlands biocontrol
Coastal Environment Centre, Pittwater Council (project lead)
 This project aimed to control the growth and further spread of Salvinia, a water weed currently choking Warriewood Wetlands EEC, through introduction of cyrtabagous weevil. Prior to introduction, mechanical and physical weed treatment was planned, to reduce Salvinia cover to improve the probability of successful establishment of the weevil. However due to storm events, a large amount of Salvinia was washed away, delivering considerable savings for the project in mechanical clear. Unfortunately, subsequent storms also washed away many weevils. A monitoring report (17MB) provides a mixed picture for the future of Salvinia weevils in the Sydney Basin, and more research is required to better understand their viability as a tool for Salvinia management here.
This project aimed to control the growth and further spread of Salvinia, a water weed currently choking Warriewood Wetlands EEC, through introduction of cyrtabagous weevil. Prior to introduction, mechanical and physical weed treatment was planned, to reduce Salvinia cover to improve the probability of successful establishment of the weevil. However due to storm events, a large amount of Salvinia was washed away, delivering considerable savings for the project in mechanical clear. Unfortunately, subsequent storms also washed away many weevils. A monitoring report (17MB) provides a mixed picture for the future of Salvinia weevils in the Sydney Basin, and more research is required to better understand their viability as a tool for Salvinia management here.
In addition this project engaged with local schools to educate students about the importance of fragile environments in terms of biodiversity and community health and enjoyment. Through helping to reduce Salvinia, an invasive species in the wetlands, the students engaged in a high level of curriculum learning, as well as understanding environmental and community issues and were empowered to become custodians of the natural environment in their locality.
SSC_27 Fisher Bay restoration
Manly Council
 This project restored a section of coastal remnant vegetation located on the Manly Scenic Walkway in Clontarf. The project site was comprised of Littoral Rainforest, listed in NSW as an Endangered Ecological Community. The works removed invasive species and revegetated with local provenance plants. The project site also has cultural significance, with several Aboriginal middens present. This afforded the opportunity to engage with the Aboriginal Heritage Office to develop a restoration project which enables the vegetation communities to be improved, whilst protecting culturally significant sites and developing interpretive signage and other educational elements. A community engagement program built the capacity of residents to value the local biodiversity and to engage with backyard habitat and garden escapes programs and undertake voluntary restoration activities on surrounding private properties.
This project restored a section of coastal remnant vegetation located on the Manly Scenic Walkway in Clontarf. The project site was comprised of Littoral Rainforest, listed in NSW as an Endangered Ecological Community. The works removed invasive species and revegetated with local provenance plants. The project site also has cultural significance, with several Aboriginal middens present. This afforded the opportunity to engage with the Aboriginal Heritage Office to develop a restoration project which enables the vegetation communities to be improved, whilst protecting culturally significant sites and developing interpretive signage and other educational elements. A community engagement program built the capacity of residents to value the local biodiversity and to engage with backyard habitat and garden escapes programs and undertake voluntary restoration activities on surrounding private properties.
SSC_28 Hollows as homes
Royal Botanic Gardens & Domain Trust (project lead)
 This project engaged and tought community members to record the attributes of hollows and trees, and to monitor wildlife use of hollows. It has deliverd an app with online database for recording hollows. After participating in a workshop, in conjunction with councils, and assisted by customised on-line resources, participants can assess the trees in their backyard, street or park. Participants can also monitor wildlife use of constructed boxes or cut-in hollows, including the attributes of the tree and the habitat (e.g. design, material). Lastly, schools were encouraged to participate to assess trees and hollows within their grounds. As a result there has been an increased understanding of hollow-bearing trees and their vital role as habitat for wildlife.
This project engaged and tought community members to record the attributes of hollows and trees, and to monitor wildlife use of hollows. It has deliverd an app with online database for recording hollows. After participating in a workshop, in conjunction with councils, and assisted by customised on-line resources, participants can assess the trees in their backyard, street or park. Participants can also monitor wildlife use of constructed boxes or cut-in hollows, including the attributes of the tree and the habitat (e.g. design, material). Lastly, schools were encouraged to participate to assess trees and hollows within their grounds. As a result there has been an increased understanding of hollow-bearing trees and their vital role as habitat for wildlife.
SSC_29 Fishermans Walk climate change connections
Warringah Council
 The project has delivered an improved wildlife corridor linking Endangered Ecological Communities of Curl Curl potentially affected by climate change, to the coastal corridor of Freshwater/McKillop Park, using the assistance of community and corporate volunteers and professional workers. Over 4,000 native plants, of over 30 different species, have been established to replace areas once degraded by Weeds of National Significance (WoNS) and other environmental weeds. A percentage of plants have been propagated from flora further north of this area, to improve climate change biodiversity resilience.
The project has delivered an improved wildlife corridor linking Endangered Ecological Communities of Curl Curl potentially affected by climate change, to the coastal corridor of Freshwater/McKillop Park, using the assistance of community and corporate volunteers and professional workers. Over 4,000 native plants, of over 30 different species, have been established to replace areas once degraded by Weeds of National Significance (WoNS) and other environmental weeds. A percentage of plants have been propagated from flora further north of this area, to improve climate change biodiversity resilience.
SSC_30 Connected Corridors for Biodiversity
Southern Sydney Region of Councils (project lead)
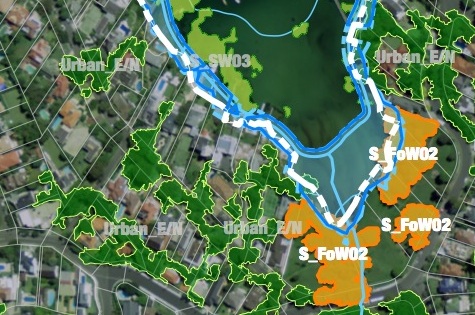
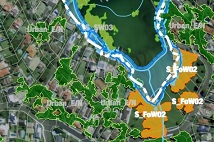 For the 23 Councils within the Sydney Coastal Councils Group (SCCG) and the Southern Sydney Region of Councils (SSROC) (including Ashfield; Bankstown; Burwood; Botany Bay; Canada Bay; Canterbury; City of Sydney; Hornsby; Hurstville; Kogarah; Leichhardt; Manly; Marrickville; Mosman; North Sydney; Pittwater; Randwick; Rockdale; Sutherland; Warringah; Waverley; Willoughby; Woollahra) existing mapping of habitat corridors, have been consolidated into one GIS layer, to identify opportunities for connectivity and contiguity across Council boundaries. This mapping layer is available online at the Greater Sydney LLS site, which will host it for 4 years, updating it annually with data from participating councils. It is supported with a summary of existing tools and programs and incentives to promote conservation on privately owned land.
For the 23 Councils within the Sydney Coastal Councils Group (SCCG) and the Southern Sydney Region of Councils (SSROC) (including Ashfield; Bankstown; Burwood; Botany Bay; Canada Bay; Canterbury; City of Sydney; Hornsby; Hurstville; Kogarah; Leichhardt; Manly; Marrickville; Mosman; North Sydney; Pittwater; Randwick; Rockdale; Sutherland; Warringah; Waverley; Willoughby; Woollahra) existing mapping of habitat corridors, have been consolidated into one GIS layer, to identify opportunities for connectivity and contiguity across Council boundaries. This mapping layer is available online at the Greater Sydney LLS site, which will host it for 4 years, updating it annually with data from participating councils. It is supported with a summary of existing tools and programs and incentives to promote conservation on privately owned land.
Climate Ready Tool
 The CSIRO SCCG partnership project, the Climate Ready Tool – Managing Coastal Ecological Communities in the Face of Rapid Changehas been a major outcome of the Salty Programme. Through a series of webinars and workshops with participating councils, this conceptual tool has been trialled and refined to assist councils in their response to climate change. Specifically it enables natural resource managers to explore the consequences of climate change for their ecological management over the long term and to scope near-term actions to start addressing those challenges. Councils can now use the tool in their planning and management.
The CSIRO SCCG partnership project, the Climate Ready Tool – Managing Coastal Ecological Communities in the Face of Rapid Changehas been a major outcome of the Salty Programme. Through a series of webinars and workshops with participating councils, this conceptual tool has been trialled and refined to assist councils in their response to climate change. Specifically it enables natural resource managers to explore the consequences of climate change for their ecological management over the long term and to scope near-term actions to start addressing those challenges. Councils can now use the tool in their planning and management.
Program Background
This project was designed to enhance the adaptive capacity of councils and the resilience of coastal habitats, foreshore and intertidal lands, responding to urban pressures and climate change. It comprised a 3-year research, capacity-building and on-ground rehabilitation program focusing on biodiversity and carbon storage in ‘salt-influenced ecosystems’ across Sydney’s coastal environments and urban waterways.
Grants were provided to support research, capacity-building and on-ground initiatives at local and sub-regional scales that addressed pressures from pollution, pests, degradation, inundation and erosion. The project filled existing gaps in research, information, strategy and prioritise areas for on-ground work. The program concluded in February 2017.
Salty Reference Group
 A reference group was convened for the program, to provide further specialist technical input, guide and/or undertake research, review prioritisation and critique/evaluate sub-projects during development and execution. Expertise in Sydney’s coastal ecosystems, ecological restoration, urban biodiversity and organisational capacity-building provides critical advice to achieve project outcomes.
A reference group was convened for the program, to provide further specialist technical input, guide and/or undertake research, review prioritisation and critique/evaluate sub-projects during development and execution. Expertise in Sydney’s coastal ecosystems, ecological restoration, urban biodiversity and organisational capacity-building provides critical advice to achieve project outcomes.
Newsletters
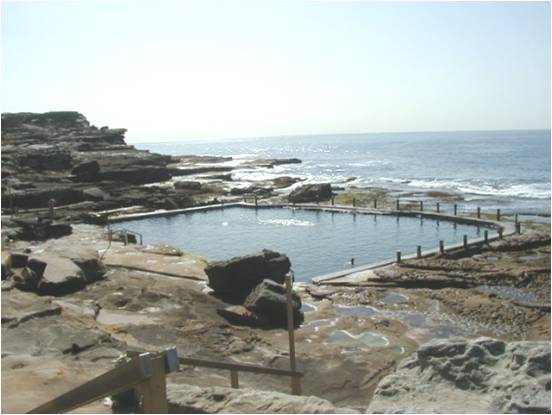




 The SCCG Member Councils face a continual challenge from settlement and growth of marine organisms (“fouling”) on coastal rock pools and platforms. The challenge arises from public health and safety concerns (and associated Council liability) for bathers who can slip on fouled surfaces. Approaches used to date primarily include mechanical cleaning and various biocides, particularly chlorine based bleaches. The use of the latter is constrained by significant concerns over non-target effects as the chlorine washes from platforms/pools into the marine environment more generally.
The SCCG Member Councils face a continual challenge from settlement and growth of marine organisms (“fouling”) on coastal rock pools and platforms. The challenge arises from public health and safety concerns (and associated Council liability) for bathers who can slip on fouled surfaces. Approaches used to date primarily include mechanical cleaning and various biocides, particularly chlorine based bleaches. The use of the latter is constrained by significant concerns over non-target effects as the chlorine washes from platforms/pools into the marine environment more generally.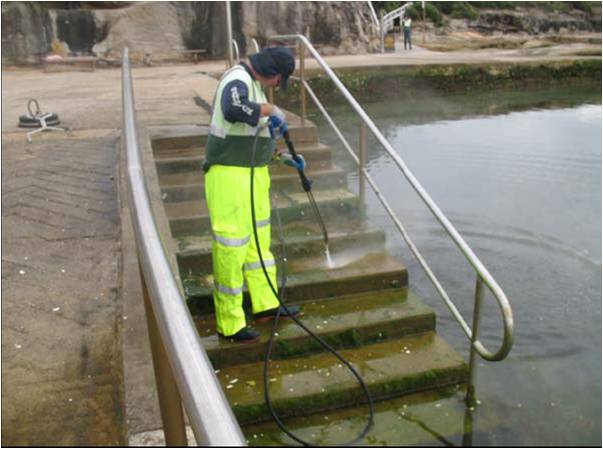 Mechanical cleaning has also not proved satisfactory because even very frequent cleaning is not sufficient to prevent fouling. This is not particularly surprising, given that microfouling – bacteria, diatoms, other microalgae – can form a slippery layer of slime with a day or two. These and other approaches to the problem are detailed in the SCCG’s 1996 discussion paper, “Finding suitable options for cleaning Sydney’s estuarine tidal baths & ocean rock pools for use by local governments”.
Mechanical cleaning has also not proved satisfactory because even very frequent cleaning is not sufficient to prevent fouling. This is not particularly surprising, given that microfouling – bacteria, diatoms, other microalgae – can form a slippery layer of slime with a day or two. These and other approaches to the problem are detailed in the SCCG’s 1996 discussion paper, “Finding suitable options for cleaning Sydney’s estuarine tidal baths & ocean rock pools for use by local governments”. In 2008, the SCCG contracted Centre for Marine Bio-Innovation Algae samples(University of New South Wales) to undertake the above mentioned project. This project was made possible with funding contributions from the NSW Department of Environment, Climate Change and Water, Randwick and Sutherland Councils together with the SCCG.
In 2008, the SCCG contracted Centre for Marine Bio-Innovation Algae samples(University of New South Wales) to undertake the above mentioned project. This project was made possible with funding contributions from the NSW Department of Environment, Climate Change and Water, Randwick and Sutherland Councils together with the SCCG. Results found that two coatings in combination with modified cleaning practices are recommended for commercial scale trials on pedestrian access points anticipating subsequent take up of these technologies. When these coatings are combined with the recommended modified cleaning practices the following improvements are expected:
Results found that two coatings in combination with modified cleaning practices are recommended for commercial scale trials on pedestrian access points anticipating subsequent take up of these technologies. When these coatings are combined with the recommended modified cleaning practices the following improvements are expected:




 In order to address the issues of continual shoreline erosion in these “at threat” sites to a point where decision makers can commit long-term physical and financial resources, it is essential to understand the environmental, physical and economical needs and feasibility of utilising offshore marine sand source for beach nourishment purposes. The task of assessing the feasibility of these aspects is detailed and complex and seeks to advance government policy on the potential use off marine resources of sand for nourishment purposes.
In order to address the issues of continual shoreline erosion in these “at threat” sites to a point where decision makers can commit long-term physical and financial resources, it is essential to understand the environmental, physical and economical needs and feasibility of utilising offshore marine sand source for beach nourishment purposes. The task of assessing the feasibility of these aspects is detailed and complex and seeks to advance government policy on the potential use off marine resources of sand for nourishment purposes. The study focuses in detail on the application of sand nourishment to the proposed case study sites: Collaroy / Narrabeen, Manly and Bate Bay (Cronulla) beaches; but also provides generic consideration of sand nourishment requirements in other areas of the Greater Metropolitan Region facing immediate threat including: Pittwater LGA – Bilgola Beach; Gosford LGA: Wamberal, North Avoca and Terrigal beaches; Newcastle LGA: Stockton Beach. Similarly the study provides a generic assessment of the sand nourishment requirements to offset the loss of recreational amenity within the Sydney Greater Metropolitan Region open coast beaches from projected rise in mean sea level due to climate change.
The study focuses in detail on the application of sand nourishment to the proposed case study sites: Collaroy / Narrabeen, Manly and Bate Bay (Cronulla) beaches; but also provides generic consideration of sand nourishment requirements in other areas of the Greater Metropolitan Region facing immediate threat including: Pittwater LGA – Bilgola Beach; Gosford LGA: Wamberal, North Avoca and Terrigal beaches; Newcastle LGA: Stockton Beach. Similarly the study provides a generic assessment of the sand nourishment requirements to offset the loss of recreational amenity within the Sydney Greater Metropolitan Region open coast beaches from projected rise in mean sea level due to climate change.








 The City of Sydney partnered with The University of Sydney’s Centre for Research on Ecological Impacts of Coastal Cities and the Royal Botanic Gardens & Domains Trust to create an aquatic corridor along the seawall foreshore of the City of Sydney local government area. This project delivered
The City of Sydney partnered with The University of Sydney’s Centre for Research on Ecological Impacts of Coastal Cities and the Royal Botanic Gardens & Domains Trust to create an aquatic corridor along the seawall foreshore of the City of Sydney local government area. This project delivered  Bush regeneration contractors were engaged to remove weed species & encourage regeneration of native species in Gore Creek Reserve, focusing on endangered Littoral Rainforest and surrounds. Weed species to be controlled in the reserve included: ground asparagus, morning glory, madeira vine, Ehrharta, Trad, Privet & Ochna. Gore Creek Reserve Bushcare group and others have worked alongside the contractors with the aim of restoring bushland adjacent to their work sites. This project has been successfully completed and the legacy of the project will be maintained in the years to come through Lane Cove Council’s commitment of ongoing designated operational budget for the area, as well as the efforts of the local BushCare groups.
Bush regeneration contractors were engaged to remove weed species & encourage regeneration of native species in Gore Creek Reserve, focusing on endangered Littoral Rainforest and surrounds. Weed species to be controlled in the reserve included: ground asparagus, morning glory, madeira vine, Ehrharta, Trad, Privet & Ochna. Gore Creek Reserve Bushcare group and others have worked alongside the contractors with the aim of restoring bushland adjacent to their work sites. This project has been successfully completed and the legacy of the project will be maintained in the years to come through Lane Cove Council’s commitment of ongoing designated operational budget for the area, as well as the efforts of the local BushCare groups.
 The North Palm Beach Dune Rehabilitation project rehabilitated 5.9ha (50% more than target) of highly degraded coastal dune within the North Palm Beach dune system. Managing weeds in the target site was important in tackling what was a reservoir of weeds threatening other rehabilitated and remnant vegetation. Over 5,000 native tubestock were planted. Completion of this project has reconnected a well-functioning native ecosystem and improved cological linkages between remnant native vegetation. This grant project has now been successfully completed and the legacy of the project will be maintained in the years to come through Northern Beaches Council’s commitment of ongoing designated operational budget for the area, as well as the efforts of local BushCare groups.
The North Palm Beach Dune Rehabilitation project rehabilitated 5.9ha (50% more than target) of highly degraded coastal dune within the North Palm Beach dune system. Managing weeds in the target site was important in tackling what was a reservoir of weeds threatening other rehabilitated and remnant vegetation. Over 5,000 native tubestock were planted. Completion of this project has reconnected a well-functioning native ecosystem and improved cological linkages between remnant native vegetation. This grant project has now been successfully completed and the legacy of the project will be maintained in the years to come through Northern Beaches Council’s commitment of ongoing designated operational budget for the area, as well as the efforts of local BushCare groups. The project addressed major weed infestations within the project area. Two EECs were targeted: Themeda Grasslands on Coastal Headlands and Littoral Rainforest & Coastal Vine Thickets. Revegetation at 3 sites controlled exotic grasses at South Bilgola Headland, providing littoral restoration of the Bilgola Creek and restoring Coastal Clay Heath within an area heavily invaded by bamboo. A
The project addressed major weed infestations within the project area. Two EECs were targeted: Themeda Grasslands on Coastal Headlands and Littoral Rainforest & Coastal Vine Thickets. Revegetation at 3 sites controlled exotic grasses at South Bilgola Headland, providing littoral restoration of the Bilgola Creek and restoring Coastal Clay Heath within an area heavily invaded by bamboo. A 
 This project has brought together 11 physically connected Councils (Bayside, Cumberland, City of Canada Bay, City of Canterbury Bankstown, Georges River, Inner West, Randwick, Strathfield, City of Sydney, Sutherland Shire & Waverley) and Royal Botanic Gardens Sydney (RBGS) to coordinate a regional approach to fox management through a Fox Control Working Committee. SSROC have taken over management of this Committee to continue its work. A web portal,
This project has brought together 11 physically connected Councils (Bayside, Cumberland, City of Canada Bay, City of Canterbury Bankstown, Georges River, Inner West, Randwick, Strathfield, City of Sydney, Sutherland Shire & Waverley) and Royal Botanic Gardens Sydney (RBGS) to coordinate a regional approach to fox management through a Fox Control Working Committee. SSROC have taken over management of this Committee to continue its work. A web portal,  The Waverley Council LGA has lost 99% of the remnant vegetation that was present before European Settlement. This project is part of a larger effort by Waverley Council to halt this loss and improve the condition of the remnant from the current 4% up to 40% by 2020. To implement Council’s newly adopted
The Waverley Council LGA has lost 99% of the remnant vegetation that was present before European Settlement. This project is part of a larger effort by Waverley Council to halt this loss and improve the condition of the remnant from the current 4% up to 40% by 2020. To implement Council’s newly adopted  and a reduction in invasive weeds, particularly along the coastal cliff-top heath vegetation communities. In combination with revegetation plantings the outcome has been an increased in size and resilience of the remnant vegetation communities. This grant project has now been successfully completed and the legacy of the project will be maintained for at least the next five years through Waverley Council’s commitment of ongoing designated operational budget for the area, as well as through the efforts of local BushCare groups.
and a reduction in invasive weeds, particularly along the coastal cliff-top heath vegetation communities. In combination with revegetation plantings the outcome has been an increased in size and resilience of the remnant vegetation communities. This grant project has now been successfully completed and the legacy of the project will be maintained for at least the next five years through Waverley Council’s commitment of ongoing designated operational budget for the area, as well as through the efforts of local BushCare groups. The project has improved connectivity between three zones located along the Lane Cove R. starting from the Fullers Rd bridge next to the Lane Cove National Park moving south through O.H. Reid Reserve, the Chatswood Golf Course and Mowbray Park. Work primarily consisted of invasive weed removal to allow natural regeneration of indigenous species and this was supplemented with some plantings of indigenous plants to strengthen connection of work zones and other saltmarsh areas along the Lane Cove R. Willoughby City Council matched the contribution from Sydney’s Salty Communities grant to deliver this important project to rehabilitate this impacted ecosystem. 2,600 native tubestock were planted (800 more than target) and 8.9ha of weed treatment was undertaken. This grant project has now been successfully completed and the legacy of the project will be maintained in the future through Willoughby Council’s commitment of ongoing designated operational budget for the area, and the ongoing relationship they have developed with Chatswood Golf Club.
The project has improved connectivity between three zones located along the Lane Cove R. starting from the Fullers Rd bridge next to the Lane Cove National Park moving south through O.H. Reid Reserve, the Chatswood Golf Course and Mowbray Park. Work primarily consisted of invasive weed removal to allow natural regeneration of indigenous species and this was supplemented with some plantings of indigenous plants to strengthen connection of work zones and other saltmarsh areas along the Lane Cove R. Willoughby City Council matched the contribution from Sydney’s Salty Communities grant to deliver this important project to rehabilitate this impacted ecosystem. 2,600 native tubestock were planted (800 more than target) and 8.9ha of weed treatment was undertaken. This grant project has now been successfully completed and the legacy of the project will be maintained in the future through Willoughby Council’s commitment of ongoing designated operational budget for the area, and the ongoing relationship they have developed with Chatswood Golf Club.
 Through this project, waste oyster shell collected from commercial farms were processed and arranged to protect eroding riverbanks and to stabilise riparian and coastal vegetation. For the purposes of the Salty Communities Program, erosion control and vegetation enhancement is the primary objective. The project was carried out on behalf of 4 councils – Willoughby, Lane Cove, Sutherland Shire and City of Ryde, and involves education, with community groups engaged in reef building activities. Macquarie University is currently undertaking research into the performance of different oyster reef structures, & will build these project sites into their research program.
Through this project, waste oyster shell collected from commercial farms were processed and arranged to protect eroding riverbanks and to stabilise riparian and coastal vegetation. For the purposes of the Salty Communities Program, erosion control and vegetation enhancement is the primary objective. The project was carried out on behalf of 4 councils – Willoughby, Lane Cove, Sutherland Shire and City of Ryde, and involves education, with community groups engaged in reef building activities. Macquarie University is currently undertaking research into the performance of different oyster reef structures, & will build these project sites into their research program. 
 Located in the Woronora River valley area (Woronora to Heathcote), the project has reduced the impacts of aggressive weed species, Weeds of National Significance & Key Threatening Processes on threatened flora and fauna species & three Endangered Ecological Communities of Coastal Saltmarsh, Swamp Oak Flood Plain Forest & Swamp Sclerophyll Forest on Coastal Floodplains. The activities have enhanced the 9 sites’ native biodiversity, increase public empowerment/knowledge and ensure past inappropriate urban development is ameliorated to ensure the ecosystem health of one of Sydney’s most unique Riverine systems. The project significantly exceeded its targets: pest management was undertaken in over 200ha of bushland (44% above target); weed treatment was implemented in 85ha (21% above target), and; over 2,100 native tubestock were planted (114% above target). This grant project has now been successfully completed and the legacy of the project will be maintained for at least the next ten years through Sutherland Shire Council’s commitment of ongoing designated operational budget for the area, as well as its long-term Woronora River Management Plan.
Located in the Woronora River valley area (Woronora to Heathcote), the project has reduced the impacts of aggressive weed species, Weeds of National Significance & Key Threatening Processes on threatened flora and fauna species & three Endangered Ecological Communities of Coastal Saltmarsh, Swamp Oak Flood Plain Forest & Swamp Sclerophyll Forest on Coastal Floodplains. The activities have enhanced the 9 sites’ native biodiversity, increase public empowerment/knowledge and ensure past inappropriate urban development is ameliorated to ensure the ecosystem health of one of Sydney’s most unique Riverine systems. The project significantly exceeded its targets: pest management was undertaken in over 200ha of bushland (44% above target); weed treatment was implemented in 85ha (21% above target), and; over 2,100 native tubestock were planted (114% above target). This grant project has now been successfully completed and the legacy of the project will be maintained for at least the next ten years through Sutherland Shire Council’s commitment of ongoing designated operational budget for the area, as well as its long-term Woronora River Management Plan. The remnant canopy of Balls Head has been affected by termites which appears to be having a serious ring-barking effect on many of these trees. To avoid generational loss of canopy this project involved research to compare treatment of arboreal termites (Nasutitermes walkeri) with appropriate control sites to compare tree responses and determine cause and effect for poor tree health. There has been a formalised monitoring regime, implemented by the
The remnant canopy of Balls Head has been affected by termites which appears to be having a serious ring-barking effect on many of these trees. To avoid generational loss of canopy this project involved research to compare treatment of arboreal termites (Nasutitermes walkeri) with appropriate control sites to compare tree responses and determine cause and effect for poor tree health. There has been a formalised monitoring regime, implemented by the  This project supported an ongoing whole-of-lagoon approach, by focussing on the southern area of the refuge through restoring saltmarsh, creating habitat linkages and controlling vertebrate pest animals. This project has • Reduced the spread of high priority weeds; • Promoted a backyard habitat and garden escapes program; • Promoted the DY Fauna Fair as a celebration of the Wildlife Refuge for lagoon users; • Established a native seed bank using provenance from Dee Why Lagoon and neighbouring lagoon systems; • Produced a condition map of the bushland and saltmarsh, including mapping tree hollows. This project complements the ‘Dee Why Lagoon Wildlife Refuge Habitat Restoration Project’, a three year program funded through Environmental Trust.
This project supported an ongoing whole-of-lagoon approach, by focussing on the southern area of the refuge through restoring saltmarsh, creating habitat linkages and controlling vertebrate pest animals. This project has • Reduced the spread of high priority weeds; • Promoted a backyard habitat and garden escapes program; • Promoted the DY Fauna Fair as a celebration of the Wildlife Refuge for lagoon users; • Established a native seed bank using provenance from Dee Why Lagoon and neighbouring lagoon systems; • Produced a condition map of the bushland and saltmarsh, including mapping tree hollows. This project complements the ‘Dee Why Lagoon Wildlife Refuge Habitat Restoration Project’, a three year program funded through Environmental Trust. This project aimed to control the growth and further spread of Salvinia, a water weed currently choking Warriewood Wetlands EEC, through introduction of cyrtabagous weevil. Prior to introduction, mechanical and physical weed treatment was planned, to reduce Salvinia cover to improve the probability of successful establishment of the weevil. However due to storm events, a large amount of Salvinia was washed away, delivering considerable savings for the project in mechanical clear. Unfortunately, subsequent storms also washed away many weevils. A
This project aimed to control the growth and further spread of Salvinia, a water weed currently choking Warriewood Wetlands EEC, through introduction of cyrtabagous weevil. Prior to introduction, mechanical and physical weed treatment was planned, to reduce Salvinia cover to improve the probability of successful establishment of the weevil. However due to storm events, a large amount of Salvinia was washed away, delivering considerable savings for the project in mechanical clear. Unfortunately, subsequent storms also washed away many weevils. A  This project restored a section of coastal remnant vegetation located on the Manly Scenic Walkway in Clontarf. The project site was comprised of Littoral Rainforest, listed in NSW as an Endangered Ecological Community. The works removed invasive species and revegetated with local provenance plants. The project site also has cultural significance, with several Aboriginal middens present. This afforded the opportunity to engage with the Aboriginal Heritage Office to develop a restoration project which enables the vegetation communities to be improved, whilst protecting culturally significant sites and developing interpretive signage and other educational elements. A community engagement program built the capacity of residents to value the local biodiversity and to engage with backyard habitat and garden escapes programs and undertake voluntary restoration activities on surrounding private properties.
This project restored a section of coastal remnant vegetation located on the Manly Scenic Walkway in Clontarf. The project site was comprised of Littoral Rainforest, listed in NSW as an Endangered Ecological Community. The works removed invasive species and revegetated with local provenance plants. The project site also has cultural significance, with several Aboriginal middens present. This afforded the opportunity to engage with the Aboriginal Heritage Office to develop a restoration project which enables the vegetation communities to be improved, whilst protecting culturally significant sites and developing interpretive signage and other educational elements. A community engagement program built the capacity of residents to value the local biodiversity and to engage with backyard habitat and garden escapes programs and undertake voluntary restoration activities on surrounding private properties. This project engaged and tought community members to record the attributes of hollows and trees, and to monitor wildlife use of hollows. It has deliverd
This project engaged and tought community members to record the attributes of hollows and trees, and to monitor wildlife use of hollows. It has deliverd  The project has delivered an improved wildlife corridor linking Endangered Ecological Communities of Curl Curl potentially affected by climate change, to the coastal corridor of Freshwater/McKillop Park, using the assistance of community and corporate volunteers and professional workers. Over 4,000 native plants, of over 30 different species, have been established to replace areas once degraded by Weeds of National Significance (WoNS) and other environmental weeds. A percentage of plants have been propagated from flora further north of this area, to improve climate change biodiversity resilience.
The project has delivered an improved wildlife corridor linking Endangered Ecological Communities of Curl Curl potentially affected by climate change, to the coastal corridor of Freshwater/McKillop Park, using the assistance of community and corporate volunteers and professional workers. Over 4,000 native plants, of over 30 different species, have been established to replace areas once degraded by Weeds of National Significance (WoNS) and other environmental weeds. A percentage of plants have been propagated from flora further north of this area, to improve climate change biodiversity resilience. For the 23 Councils within the Sydney Coastal Councils Group (SCCG) and the Southern Sydney Region of Councils (SSROC) (including Ashfield; Bankstown; Burwood; Botany Bay; Canada Bay; Canterbury; City of Sydney; Hornsby; Hurstville; Kogarah; Leichhardt; Manly; Marrickville; Mosman; North Sydney; Pittwater; Randwick; Rockdale; Sutherland; Warringah; Waverley; Willoughby; Woollahra) existing mapping of habitat corridors, have been consolidated into one GIS layer, to identify opportunities for connectivity and contiguity across Council boundaries.
For the 23 Councils within the Sydney Coastal Councils Group (SCCG) and the Southern Sydney Region of Councils (SSROC) (including Ashfield; Bankstown; Burwood; Botany Bay; Canada Bay; Canterbury; City of Sydney; Hornsby; Hurstville; Kogarah; Leichhardt; Manly; Marrickville; Mosman; North Sydney; Pittwater; Randwick; Rockdale; Sutherland; Warringah; Waverley; Willoughby; Woollahra) existing mapping of habitat corridors, have been consolidated into one GIS layer, to identify opportunities for connectivity and contiguity across Council boundaries. 
 A reference group was convened for the program, to provide further specialist technical input, guide and/or undertake research, review prioritisation and critique/evaluate sub-projects during development and execution. Expertise in Sydney’s coastal ecosystems, ecological restoration, urban biodiversity and organisational capacity-building provides critical advice to achieve project outcomes.
A reference group was convened for the program, to provide further specialist technical input, guide and/or undertake research, review prioritisation and critique/evaluate sub-projects during development and execution. Expertise in Sydney’s coastal ecosystems, ecological restoration, urban biodiversity and organisational capacity-building provides critical advice to achieve project outcomes.


